1. Describe the current machine situation and sort out:
| machine | IP | username | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10.49.**.** | user/192.168.**.**/root | Target server (Intranet) |
| B | 139.198.**.** | root | Extranet (In my case I use QingCloud) The server is equivalent to a bridge |
2. Solution:
First we start a reverse proxy of machine B on machine A; then the forward proxy on machine B realizes the forwarding of the local port.
2.1 Preparation before implementation
Each must install the ssh client.
Here I am using CentOS7, which comes with ssh. If you are using other versions of Linux, please manually Google it.
2.2 Introduce the ssh parameters used:
Reverse proxy:
ssh -fCNR
Forward agent:
ssh -fCNL
-f execute ssh command in the background
-C Allow compressed data
-N do not execute remote commands
-R Forward a port on the remote host (server) to the specified port on the local designated machine
-L forward a port on the local machine (client) to a designated port on a remote designated machine
-p specifies the port of the remote host3. First operate on A:
Establish a reverse proxy from machine A to machine B. The specific instructions are
ssh -fCNR [B machine IP or omitted]: [B machine port]: [A machine IP]: [A machine port] [Login B machine username@ServerIP]A better way to keep the SSH connection alive is to use the autossh command which can be installed with yum install autossh:
autossh -M [monitor port] -fCNR [B machine IP or omitted]: [B machine port]: [A machine IP]: [A machine port] [Login B machine username@ServerIP] Here I use the 2515 port of the B machine and the 22 port of the A machine. According to the above instructions, this is the operation.
autossh -M 2516 -fCNR 2515:localhost:22 B Verify that it is ready to use ps aux | grep ssh Instructions on A to view:
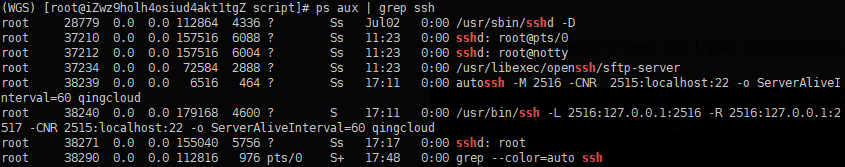
You may also want to test the connection on B using:
ssh localhost:25154. Then operate on B:
Establish a forward proxy for machine B, which is used for forwarding. The specific instruction is
ssh -fCNL [A machine IP or omitted]: [A machine port]: [B machine IP]: [B machine port] [Login B machine user name @B IP]According to the instruction entered there, the port of the B machine here is the same as the port of the B machine above, and the port 1234 is also the B machine.
ssh -fCNL *:2514:localhost:2515 localhostCheck whether it is ready to use ps aux | grep ssh Instructions to view.
Here, the 2514 port is a local forwarding port, which is responsible for communicating with the external network and forwarding data. The 2515 port realizes a function that can be accessed from other machines. At the same time, the * indicates that it can accept any IP access.
5. Time to show miracles
So far we have configured the AB machine, then we can log in from an external computer to the internal network. Since my current computer is on the internal network and the servers are all on the external network (that is, the configured B machine), I can connect to A on my internal network through the B machine. The specific instructions are:
ssh -p2515 139.198.**.** (address of B) Here, the -p parameter is the specified login IP. We specified port 1234 as the forwarding port above, so log in with port 2514, then root is the user name of the intranet A machine, and 139.198.**.** is the IP address of the extranet B machine.
Leave a Reply